Bluetooth Architecture/Network
Page Contents


There are two types of Bluetooth network
-
Piconets
-
Scatternets
Piconets
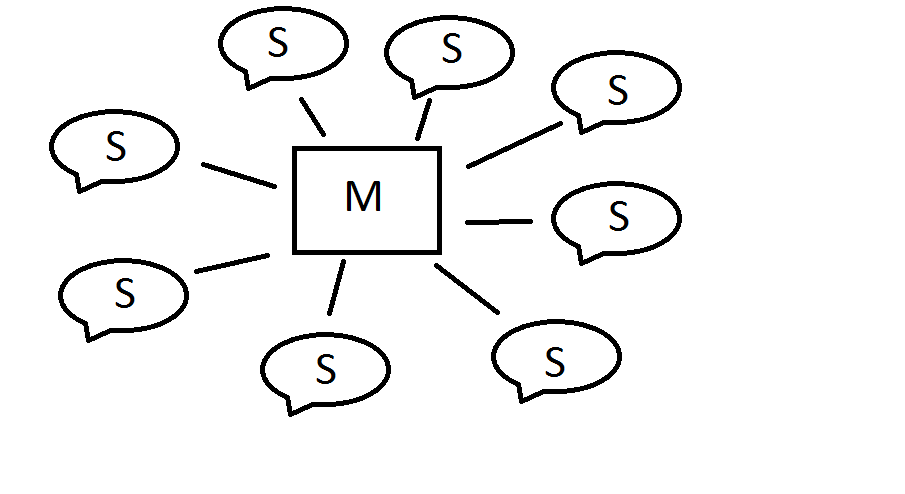
The first type of Bluetooth network is called as a piconet or a small net. It can have at the most eight stations.
One of them is called as a master and all others are called as Slaves.
All the slave’s stations are synchronized in all aspects with the master.
A piconet can have only one master station shows piconet. A master can also be called as a primary station and slaves are the secondary station.
Bluetooth Architecture
The communication between a master and slaves can be one-to-one or one-to-many. Note that the communication takes place between the master and slaves but no direct
Each master and slave has a 48-bit unique device address known as BD_ADDR that is fixed always
Note: The communication takes place between the master and slaves but no direct communication takes place between slaves.
The formation of a piconet is governed by two factors:
-
Address of each Bluetooth device.
-
Clock associated with each device.
Every device in a piconet has been assigned with a 48-bit address which is similar to an Ethernet address. The address field is divided into three parts and the Lower Address Part (LAP) is used for the purpose of piconet identification, error checking, and security checks.
Every device has a 28-bit clock which is called as a native clock. Its frequency is 3200 pulses per second i.e. once in 3.12uS, because this is exactly twice the normal hopping rate of 1600 hops/second.
A piconet can have up to seven active slaves at any given instant of time. In order to identify a slave, each one is assigned a locally unique active member address AM-ADDR.
If a Bluetooth device is not associated with any piconet, then it is said to be in standby mode.
Scatternets
Many piconets may exist simultaneously in a given area and they may even overlap each other.
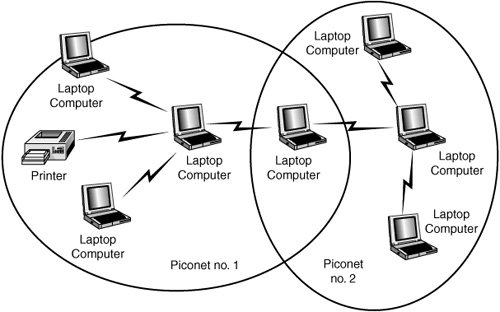
A scatternet is obtained by combining piconets as shown in fig.
Bluetooth Architecture
Also read:
Language Processors (The Interpreter) System Programing
Gyrator in Microwave Engineering
What is system Programming?
The fig shows a scatternet consisting two piconets. A slave in the first piconet can act as a master in the second piconet. It will receive the messages from the master in the first piconet by acting as a slave and then delivers the message to the slaves in the second piconet as shown in the figure. So the Number of piconets, the possibility of collisions increases.
This will result in degradation of performance.
Therefore a device can participate in two or more piconets by means of the time-sharing the process. To do so it must use the associated master’s address and proper clock offset.
Bluetooth architecture protocol and applications
A Bluetooth architecture device can act as a scatternet in that the utilization of bandwidth is not optimal. This happens because a device changes its role and takes part in different piconets. Another important issue is the timing that a device would be missing when it participates in more than one piconets. If a master of one piconet temporarily becomes a slave in some other piconet then it will be missing from its own piconet for that much time, This reduces the quality of the Bluetooth link.
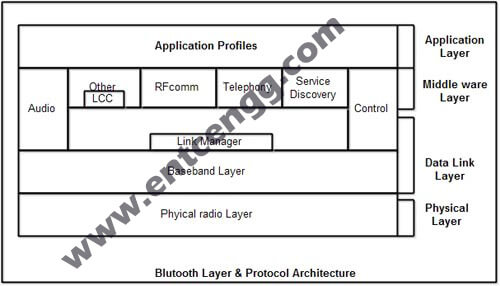
Bluetooth layers and Protocol Stack
You can also download Bluetooth architecture pdf from the link in the description of the video





