What is Management?
Page Contents
Manage-Men-tactfully
- Field of Study
- Management principles, techniques, functions
- Profession
- Team or Class of people
- Individual who performs managerial activities or maybe a group of persons
- Process
- Managerial activities
- Planning, Organizing, Staffing, Directing, Controlling.
Basics of Management
Agenda
- Concept of Management
- Definitions
- Objective and Importance of Management
- Management as an Art and a Science
- Functions of Management
- Principles of management
- Forms of Organization
- Globalization
Characteristics of Management
- Management Is a Process
- Management Is multidisciplinary
- Management Involves Group Effort.
- Management Aims at achieving predetermined objectives.
- Management is Situational in nature
- Management Is a Profession
- Management Is comprised of functions
- Management Is an art and science
Management as Art and Science
“oldest of the arts and youngest of the sciences”
Management as an Art
- Creative
- Individual approach, application, and dedication
- Intuitions, experience, imagination
- Initiative and Inventions
Management as Science
- Logical consistency
- Systematic explanation
- Evaluation
- Experimental analysis
Definitions of Industrial Management
Harold Koontz
Management is an ART of getting things done through and with the people in formally organized groups.
F.W. Talyor
Management is knowing exactly what to do, when to do and see that it is done in the best and cheapest way.
Henry Fayol
To manage is to forecast, to plan, to organize, to command, to co-ordinate and to control
Objectives of Management
Achieving Maximum results with minimum efforts
The main Objectives of Industrial Management are:
- Achieving Maximum results with minimum efforts
- Increasing the Efficiency of factors of Production
- Maximum Prosperity for Employer & Employees
- Human betterment & Social Justice
- Obtain harmony in group action
- Achieve co-operation of human beings, rather than chaotic situations
- Work for maximum output
- Proper utilization of resources(4m’s)
- Planning for future
- Mobilizing best talent
To achieve maximum output with minimal efforts, manpower, and resources.
Utilizing all the available financial resources, human resources, and Material resources efficiently so as to get the best possible results out of the above combination.
Eventually reducing the overall cost of various things.
Increasing the Efficiency of factors of Production
With the proper utilization of all the available resources, the efficiency can be increased exponentially.
Avoiding/reducing wastage, spoilage, and breakage of all kinds contribute a lot in saving time, money and efforts.
Money, time, and efforts are essential for the growth and development of an industry.
Maximum Prosperity for Employer & Employees
Management ensures the coordination and smooth function of the enterprise.
This in return provides maximum benefits to the employees.
Good working condition, Stable, and suitable wage system.
Incentives to the employee and higher profits for the employer on the other hand.
Human betterment & Social Justice
How can management help in the betterment of society?
Management acts as an important tool for the betterment and upliftment of society.
Increased number of employment and productivity contributes to society.
It ensures a better standard of living of the society and provides justices with its uniform policies.
Importance of Management
- Meet challenges of change
- Accomplish group goals
- Reduces Costs
- Establishes Sound Organization
- Optimum Utilization of Resources
- Establishes Equilibrium
- Essentials for Prosperity of Society
- Effective utilization of group goals
- The smooth functioning of business
- Identifying and developing resources
- Integrate efforts of various groups
Let us look into the above points in detail.
Meet challenges of change
Change is the only constant and management helps to meet up these challenges effectively.
Accomplish group goals
Management arranges factors of production, assembles, and organizes the resources and all the resources are integrated to achieve goals. All the group efforts are directed to the predetermined goals.
The objective of the organization once defined correctly, there would be no wastage of time efforts and money.
The disorganized resources of machines, men, and effort are converted into useful resources with the help of Management.
All these resources are directed, coordinated, and controlled in a way that the organization works towards achieving the goals.
Reduces Costs
Proper planning gives maximum results with minimum output.
Management uses the available financial, human, and physical resources in such a way that the best results are obtained.
This helps in cost reduction.
Establishes Sound Organization
No overlapping of efforts because of smooth and coordinated functions.
Sound Organization structure is one of the objectives of management.
What is Sound Organization Structure?
It Establishes Authority and responsibility i.e. the tasks and roles are preassigned. Who is accountable to whom, Who can give instructions to whom, Who are superiors & Who are subordinates?
Management recruits the right people with the right skill set, training, and qualification.
All the jobs and tasks should be cleared to everyone.
Establishes Equilibrium
Establishing an equilibrium enables the organization to survive in a changing environment.
It keeps updated with the changing environment. With the external change in the environment, the coordination of the organization should also be changed. To ensure that the organization adapts to the change in the market and needs of the society.
Essential for the growth and survival of the organization.
Essentials for Prosperity of Society
Good Management makes tough tasks easier.
Avoiding wastage, spoilage, and breakage of scarce resources.
Efficient management efforts lead to better economic production, which eventually leads to the welfare of people and society.
It improves the standard of living.
It increases the profit of the organization which leads to better wages of the employee and eventually contributing to the society by maximizing the output with minimum input cost creating employment opportunities increasing income in hands.
Organization comes with new products and researches beneficial for society.
Management Process
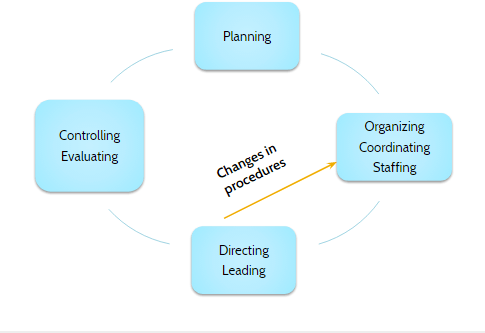
Functions of management
- Planning
- Setting goals and deciding the best method to achieve them
- The base for other functions of management
- It is a continuous process.
- Planning may be of two types:
- Strategic planning (long term)
- Operational planning (short-term)
Purpose of Planning
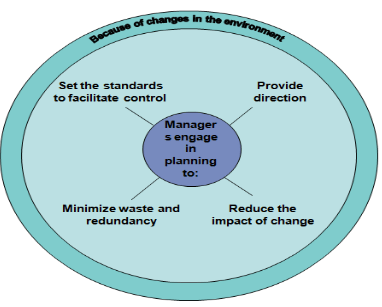
Definition of Planning
According to Koontz & O’Donnell, “Planning is deciding in advance what to do, how to do and who is to do it.
Steps in planning
- Identifying opportunities
- Setting objectives / goals
- Considering planning premise
- Identification of objective
- Identifying alternatives
- Evaluation and Choice of an alternative plan
- Setting up the priority
- Contingency Plan
Functions of management
- Organizing
- Execution of the plan step by step
- Organize the resources
- Assigning work to the groups of people
- Delegation of authority and responsibility
- determination of activities required to achieve goals;
- grouping of these activities into departments;
- provision for coordination horizontally and vertically in the
- organization
- Staffing
- Planning for human resource requirement
- Selecting, recruiting, training, and developing employees.
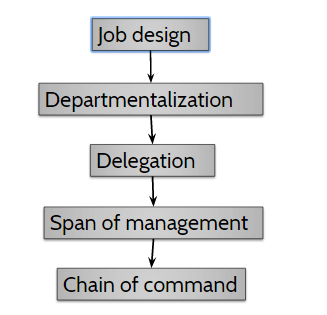
Organizational Process
- Job design
- Departmentalization
- Delegation
- Span of management
- Chain of command
Functions of management
- Directing or leading
- A manager has to be a leader
- Direct his team to achieve organizational goals
- Motivation, communication, guidance, and encouragement to his team.
- Initiate actions
- Integrate efforts
Also, Read
Circular Convolution Matlab Code Program (DSP)
Speech Recognition Using DSP Processor [Case Study]
Motivation

Motivation Theories
- Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory
- Herzberg’s two factor theory
- McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y
- McClelland achievement theory of motivation
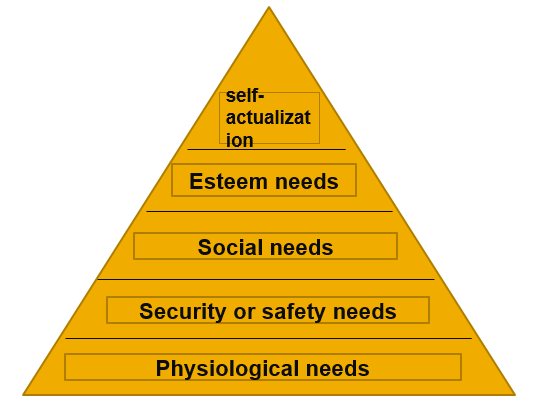
Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory
McGregor’s theory X and theory Y
- Theory X:
- Negative theory
- Assumes that workers are lazy, need to compel, they have little ambition and capacity.
- Theory Y:
- Positive theory
- Workers do not dislike work
- Self-motivated
- Creative and self- driven
McClelland’s achievement theory of motivation
- Need for achievement
- Need for affiliation
- Need for power
Functions of management
- Controlling
- Monitor the ongoing activities
- It is a process of assigning, evaluating and regulating resources on an ongoing basis.
- It is a process to measure the deviation between the planned activity and actual execution
- Measure real performance
- Ex: financial control, budget control, HR control, marketing control
Communication
- Exchange of messages between people for the purpose of achieving common meanings
- Acquire information
- Involves communication between individuals at a personal level and formal interaction too.
- Required to connect the organization with the outside world
Decision Making
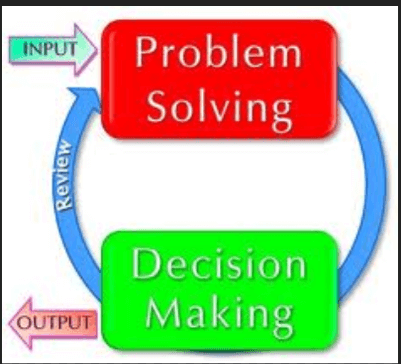
- Decision making is the process through which managers identify organizational problems and attempt to resolve them
- Steps in decision making
- Identify the problem
- Generate alternative solutions
- Evaluate and choose among alternatives
- Implement and monitor the chosen solution
- Factors affecting the decision-making process
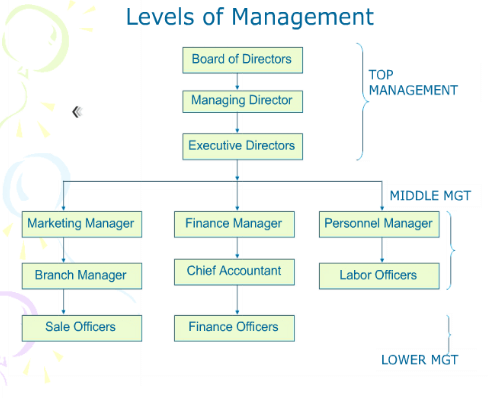
Levels of management
Management and administration
- According to Theo Haimann,
“Administration means overall determination of policies, setting of major objectives, the identification of general purposes and laying down of broad programmes and projects”.
- It refers to the activities of a higher level.
- Management is the art of getting things done.
Comparison between Management and Administration
The difference between Management and Administration can be summarized under 2 categories: –
- Functions
- Usage / Applicability
Importance of Principles of management
- Milestones of Management Practice
- Scientific management theory by F.W. Taylor
- Administrative theory by Henry Fayol
- Human Relations Theory by Elton Mayo and Hennery Gantt
F. W. Taylor’s Scientific Management Theory
- Taylor’s philosophy focused on the belief that making people work as hard as they could was not as efficient as optimizing the way the work was done.
- He proposed that by optimizing and simplifying jobs, productivity would increase.
- He also promoted the idea of “a fair day’s pay for a fair day’s work.”
Basic elements of Scientific Management
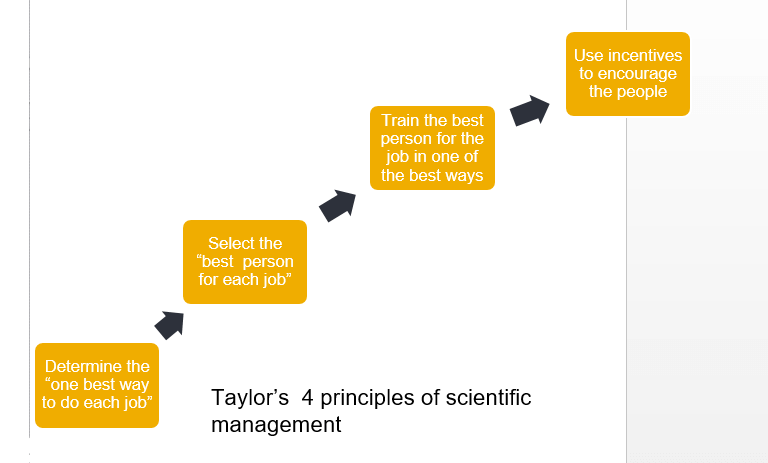
Four Principles of Scientific Management
- Replace working by “rule of thumb,” or simple habit and common sense, and instead, use the scientific method to study work and determine the most efficient way to perform specific tasks.
- Rather than simply assign workers to just any job, match workers to their jobs based on capability and motivation, and train them to work at maximum efficiency.
- Monitor worker performance, and provide instructions and supervision to ensure that they’re using the most efficient ways of working.
- Allocate the work between managers and workers so that the managers spend their time planning and training, allowing the workers to perform their tasks efficiently.
- Provide sufficient monetary incentives to the workers to perform the task correctly and efficiently.
Principles laid by Henry Fayol
- Managers in the early 1900s had very few external resources to draw upon to guide and develop their management practice.
- Henry Fayol (1841-1925), managers began to get the tools they needed to lead and manage more effectively. Fayol, and others like him, are responsible for building the foundations of modern management theory.
14 principles as the general principles management
- Division of work
- Authority and Responsibility
- Discipline
- Unity of command
- Unity of direction
- Subordination of individual interest to the general interest
- Remuneration (payment/compensation) of personnel
- Centralization
- Scalar Chain (line of authority)
- Order
- Equity
- Stability of tenure of personnel
- Initiative
Esprit de corps- “Union is strength”
Major outcomes of Elton Mayo studies
- Workers working in a group develop a bond of relationship
- Behavior at the workplace depends on their mental state, emotions, and prejudices
- Emotional factors play an important role
- Human and liberal attitude helps in improving performance
- Managerial skills and technical skills are not necessary to be a leader
Forms of Organization
Line organization
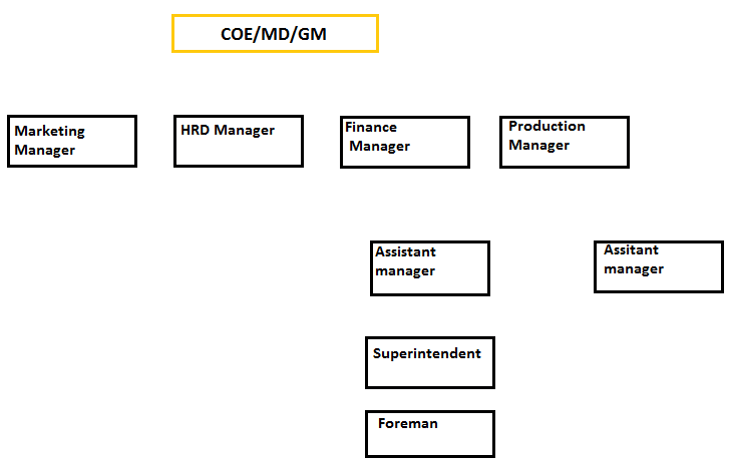
Advantages of line organization
- Easy to establish and operate
- No confusion or ambiguity
- Clear definition of authority and responsibilities
- Discipline (unified command)
Business Ownership
- Sole proprietorship
- Partnership
- Joint stock company
- Private limited company
- Public limited company
- Co-operative enterprises
- Government Sector
Proprietorship
- These firms are owned by one person.
- The owner retains absolute control over the business
- Prime motive: Profit
- Applicable for small scale business
- Least legal complications
- Drawbacks: limited skill, capital, high risk
Partnership
- Two or more people come and start a business with their own funds.
- The parties agree to share profit as well as loss in agreed proportion
- Formation of partnership is governed by the Indian Partnership Act 1932
Joint Stock Company
- A joint-stock company is a business entity which is owned by shareholders.
- Large number of people contribute capital in form of shares
- JSC are further classified as
- Private Limited Public Limited
Private limited company
- A private company limited by shares usually called a private limited company
- It can be established with two to 50 members
- The company is registered under Indian company Act 1956
- They need not submit balance sheet and audited papers to government
Public Limited company
- Common people can also be members of PLC
- PLC are supervised and controlled by Government to protect the share of shareholders
- The shares are transferable without prior approval
A private limited company’s disclosure requirements are lighter, but for this reason, its shares may not be offered to the general public (and therefore cannot be traded on a public stock exchange). This is the major distinguishing feature between a private limited company and a public limited company.
Co-operative society
- Their motive is to provide assistance to people
- It is based on democratic principles and functions for public welfare
- Not profit oriented
- Examples: Housing co-operative society
- Consumer co-operative societies
Public Sector
- Government departments
- Railways, Post Offices, Defense
- Public Corporations
- LIC, GIC, Indian Airlines
- Government Company
- HPCL, Hindustan Machine Tools, Bharat Petroleum, BARC
Globalization
- Globalization is the process of international integration arising from the interchange of world views, products, ideas, and other aspects of culture.
- The emergence of an international network of social and economic systems
Globalization of Markets
- It is a process of integrating and merging of distant markets.
- Example: Mc Donald’s, MTV, Coca-Cola, Pepsi
- These companies have different market strategies for different countries.
Globalization of Products
- It refers to the sourcing of goods and services from different locations across the globe
- It may be labor, energy, capital, etc.
- Example: Mobile phones, Automobiles
Also read:
Class Diagram for Hospital Management System
How much space does Fortnite take up?






