Language
Processors
Page Contents
Introduction
- 1.Language processing activities arise due to the differences between the manner in which a software designer describes the ideas concerning the behavior of software and the manner in which these ideas are implemented in computer system.
- 2.The designer expresses the ideas in terms related to the application domain of the software.
3.To implement these ideas, their description has to be interpreted in terms related to the execution domain.
Semantic
Gap
The term semantics to represent the rules of meaning of a domain, and the term semantic gap to represent difference between the semantics of two domains.
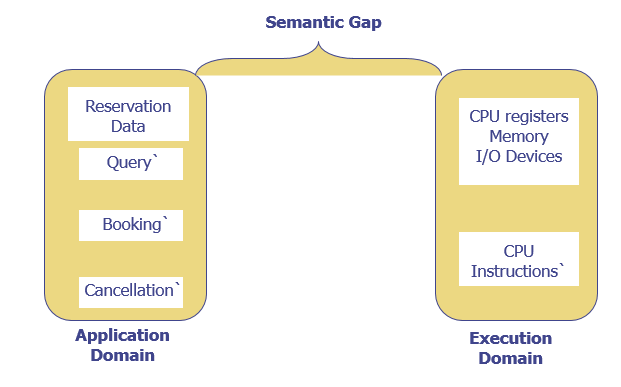
The semantic gap has many consequences, some of the important are
- Large development times
- Large development effort
- Poor quality software.
Key Software engineering steps
- Specification and design of an application program, followed by its coding in a programming language Execution of the program with the help of language processor
- An Application program written in a programming language is governed by semantics of a programming language.
- Thus use of programming language has introduces a new domain, programming language domain PL Domain.
Specification and execution Gap
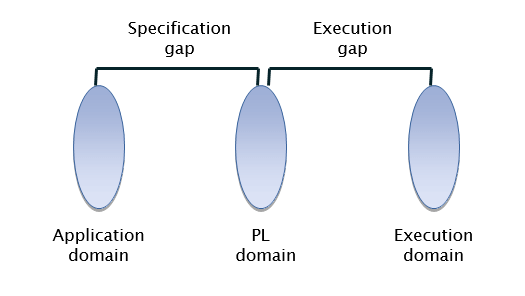
Specification Gap:
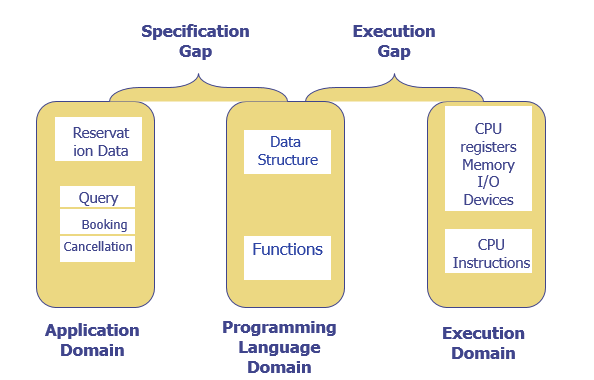
and procedure oriented programming languages
Lets a user specify a computation using data and operation that are meaningful in the area of the computation
Language
Processors
- A language processor is software which bridge a specification or execution gap.

Language processor abandons generation of target program if it detects error in the source program
- A Language Translator
- De-translator
- Preprocessor
- Language migrator
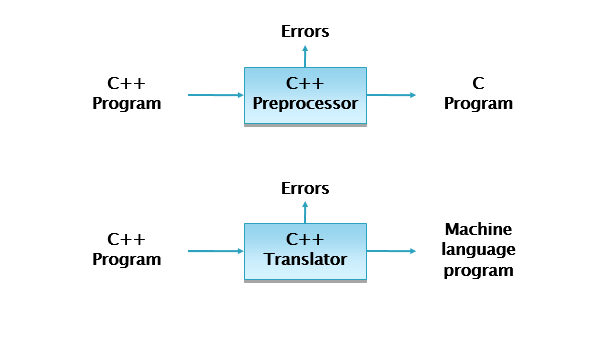
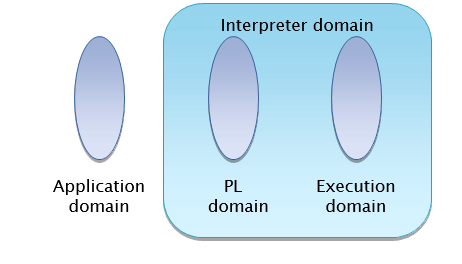
Interpreter
An interpreter is language processor which bridges an execution gap without generating a machine language program that means the execution gap vanishes totally.
Fundamental activities divided into those that bridge the specification gap and execution gap.
- Program generation activities
- Program execution activities
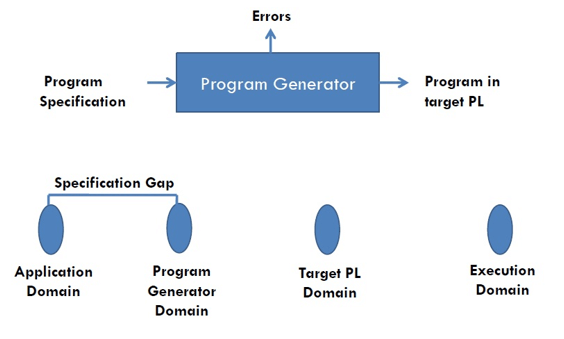
Program Generation:
- A program generation activity aims at automatic generation of a program.
- A source language is a specification language of an application domain and the target language is procedure oriented PL.
- Program generator introduces a new domain between the application and PL domain, call this the program generator domain.
- Specification gap now between Application domain and program generation domain, reduction in the specification gap increases the reliability of the generated program.
Also read GATE MCQ’s
There are 2 popular models of program execution
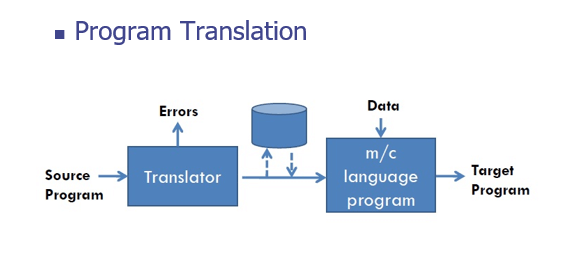
1.Program Translation
2.Program Interpretation
Lets us know briefly about these two,
Program Translation:The program translation model bridges the execution gap by translating a sources program into program in the machine or assembly language of the computer system, called target program.
Characteristics of the program translation model:
- A program must be translated before it can be executed
- The translated program may be saved in a file. The saved program may be executed repeatedly.
- A program must be retranslated following modifications.
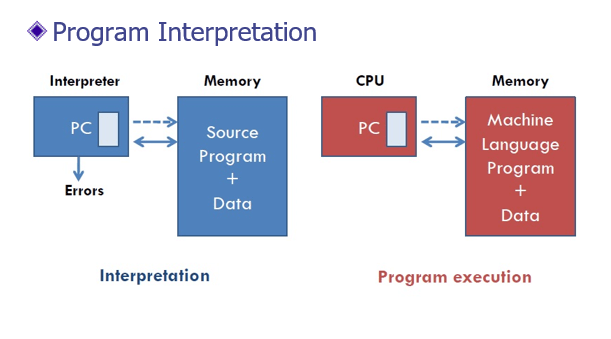
Program Interpretation: during interpretation interpreter takes source program statement, determines its meaning and performs actions which implement it.
The function of an interpreter is same as the execution of machine language program by CPU.
- The source program is retained in the source form itself, no target program form exists,
- A statement is analyzed during its interpretation.
Comparison
- In translator whole program is translated into target and if modified the source program, whole source program is translated irrespective to size of modification.
- That not the in case of interpreter, interpretation is slower than execution of m/c language program.